Research Project on Cybersecurity
1. Detection and monitoring malicious applications on android mobile devices (funding by the national broadcasting and telecommunication commission : NBTC during 2016-2017)
a. Static analysis for malware detection by using machine learning
b. Behavioral detection of malicious code on mobile operating systems
b. Behavioral detection of malicious code on mobile operating systems
2. Virtual learning center of cyber-securities awareness for home-users (funding by the national broadcasting and telecommunication commission : NBTC in 2017)
a. Extracting information approach from on-line news
b. Web-based retrieval systems for on-line news
c. Web-based training systems for cyber-securities awareness
d. Game-based learning environment for children and youth
e. Information Visualization of cyber-crimes
Research Detail:
1. Detection and monitoring malicious applications on android mobile devices (funding by the national broadcasting and telecommunication commission : NBTC during 2016-2017)
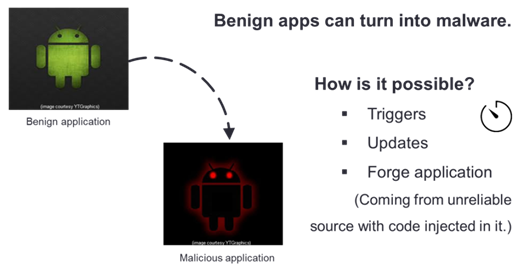
a. Static analysis for malware detection by using machine learning
This research focuses on a model for malware detection on mobile operating system based on machine learning technique. The objective is to reduce the risk of installing harmful application when the user did not update the anti-virus program in time. The proposed model is different to other anti-virus is that most of anti-virus software used virus signature to identify malware. However, the virus signature-based detection approach requires frequent updates of the virus signature dictionary. The signature-based approaches are not effective against new, unknown viruses while the proposed model based on machine learning can detect new malware even some parts of the code have been modified.

b. Behavioral detection of malicious code on mobile operating systems
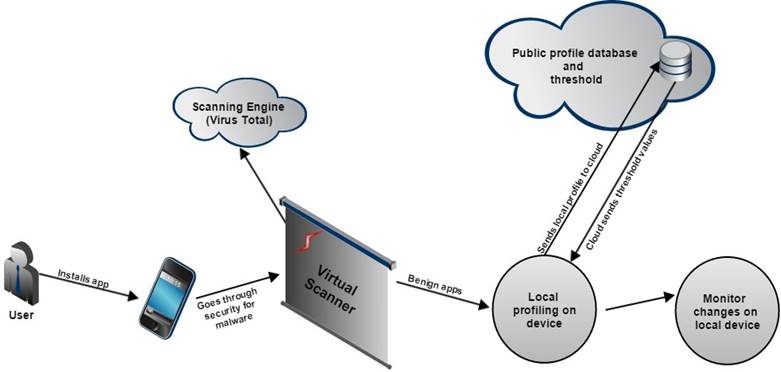
This research focuses on earlier approaches for dynamic analysis of application behavior as a means for detecting malware in the Android platform. The detector is embedded in an overall framework for collection of traces from an unlimited number of real users based on crowdsourcing. Our framework has been demonstrated by analyzing the data collected in the central server using two types of data sets: those from artificial malware created for test purposes, and those from real malware found in the wild.
2. Virtual learning center of cyber-securities awareness for home-users
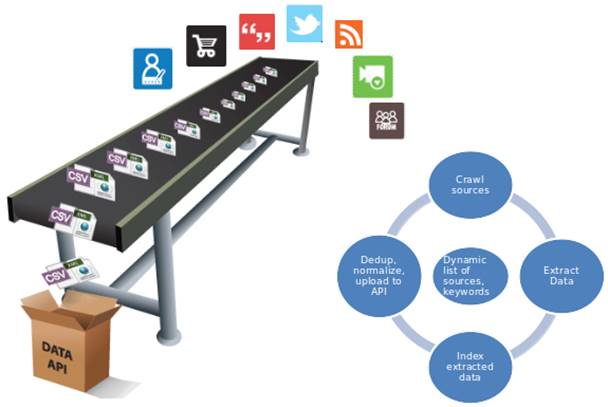
a. Extracting information approach from on-line news
In many real-world scenarios, the ability to automatically classify documents into a fixed set of categories is highly desirable. Common scenarios include classifying a large amount of unclassified archival documents such as newspaper articles, legal records and academic papers. For example, newspaper articles can be classified as ‘crimes’, ‘cyber-crimes’, ’features’, ’sports’ or ’news’. Other scenarios involve classifying of documents as they are created. Examples include classifying movie review articles into ’positive’ or ’negative’ reviews or classifying only blog entries using a fixed set of labels.
Natural language processing offers powerful techniques for automatically classifying documents. These techniques are predicated on the hypothesis that documents in different categories distinguish themselves by features of the natural language contained in each document. Salient features for document classification may include word structure, word frequency, and natural language structure in each document. This project looks specifically at the task of automatically classifying newspaper articles in “cyber-crimes” from news feeds.
b. Web-based retrieval systems for on-line news
This project discusses a system for online new event detection in the domain of news articles on the web. This area is related to the Topic Detection and Tracking initiative. We evaluate two benchmark systems: The first like most current web retrieval systems, relies on term repetition to calculate document relatedness. The second attempts to perform conceptual indexing through the use of the WordNet thesaurus software. We propose a novel approach for the identification of breaking news stories, which uses a technique called lexical chaining. We believe that this technique will improve the overall performance of our web retrieval system by allowing us to encapsulate the context surrounding a word and disambiguate its senses.
c. Web-based training systems for cyber-securities awareness
Web-based training (sometimes called e-learning) is anywhere, any-time instruction delivered over the Internet to browser-equipped learners. There are two primary models of Web-based instruction: synchronous (instructor-facilitated) and asynchronous (self-directed, self-paced). Instruction can be delivered by a combination of static methods (learning portals, hyperlinked pages, screen cam tutorials, streaming audio/video, and live Web broadcasts) and interactive methods (threaded discussions, chats, and desk-top video conferencing).
d. Game-based learning environment for children and youth
A new interest in the use of games for learning has emerged, and a number of claims are made with respect to the effectiveness of games in education. These educational games are considered as new instructional technology with great potential. The suggested positive outcomes and effects have been mentioned repeatedly. In this project, the educational game for teaching how to use Internet and playing social network are studied and developed in order to gain more insights into the conditions under which a game may be effective for learning. A systematic literature search in three databases was conducted. Some studies reported a positive effect on learning and motivation, but this is moderated by different learner variables and depends on different context variables. Next to this, the effectivity research on game-based learning is highly susceptible to a muddle of approaches, methodologies, and descriptions of gaming for educational purposes.
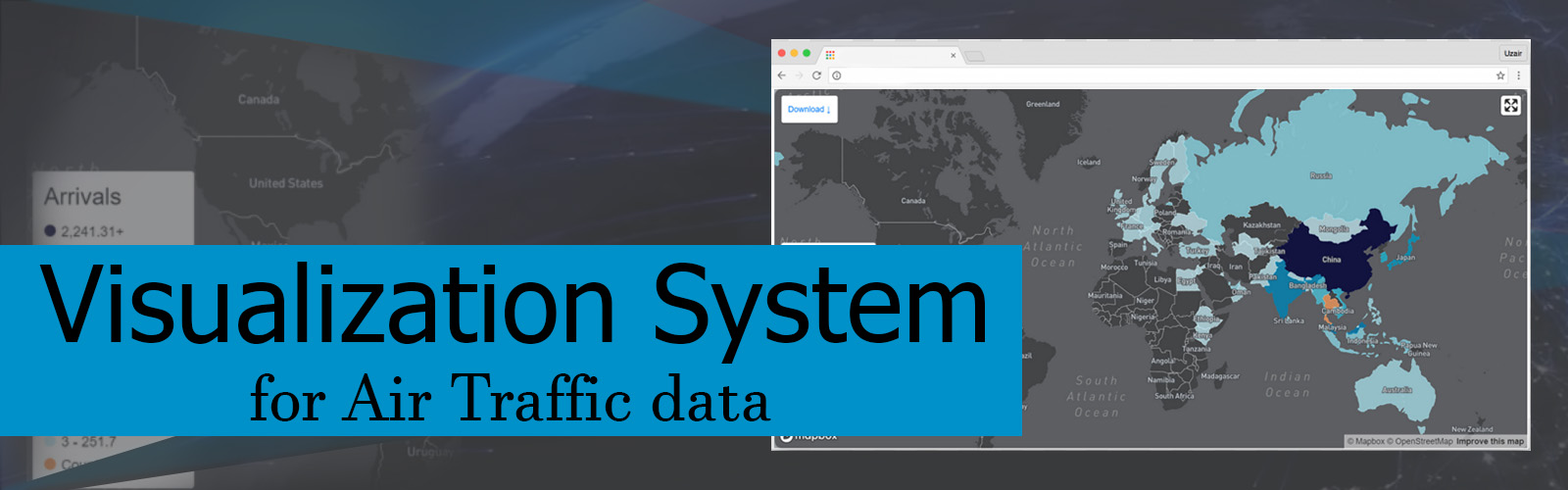
e. Information Visualization of cyber-crimes
Information visualization or information visualization is the study of (interactive) visual representations of abstract data to reinforce human cognition. The abstract data include both numerical and non-numerical data, such as text and geographic information. The field of information visualization has emerged "from research in human-computer interaction, computer science, graphics, visual design, psychology, and business methods. This project focuses on displaying the statistics of cyber-crimes in a way of interesting presentation to audiences.