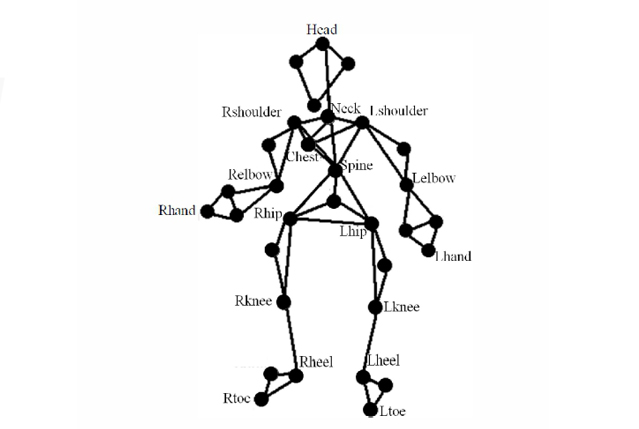
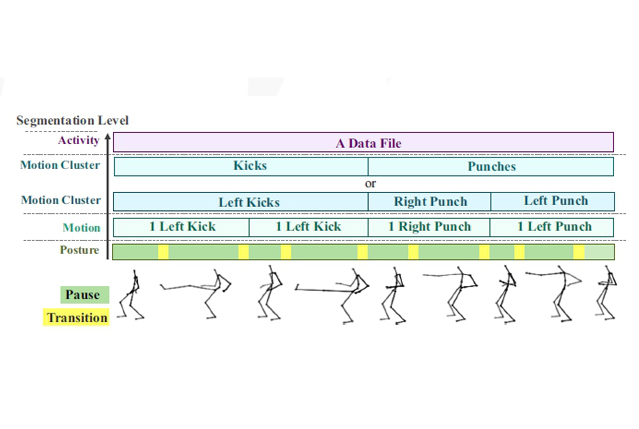
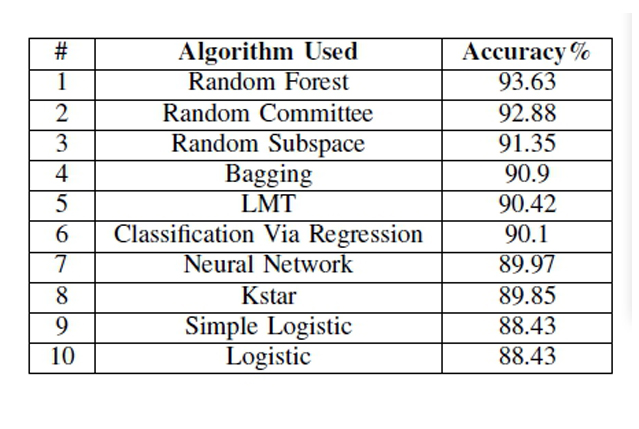
AUTHORS: Chonthorn Ariyapitipan and Kingkarn Sookhanaphibarn
ABSTRACT: This paper presents a systematic approach for video-audience-watching content analysis. Our analysis technique is based on audience preference that they will click Like while watching a video clip. The principal component analysis is applied to extract the content structure of a video clip. The hierarchical clustering technique also is used to segment a video content as time slots. The analysis and clustering are based on the audience opinion. In our experiment, the approach is set to teaching video content for 22 4-year students in Bachelor degree. The analysis results show the three principal structures that can represent three principal video-audience-watching preference styles.